Rotation planting for the Vegetable Garden
Crop rotation in the vegetable garden is an important aspect of plant health, it differs from companion planting. This is nothing new, gardeners have been using the practice for centuries.
The basic of rotation planting revolve around sequencing planting over a 4 year period. This means that plants are grouped together in four groups Legumes. Root Vegetables, Leafy Greens and Fruit bearing Plants. Each year the group is shifted on to the next plot. Related plants such as tomato and potato also do not follow each other.
So if you divide you veggie garden into four sections you are ready to start rotating crops.
Benefits of Rotation Planting
The idea is that by rotating crops you will achieve
- improved soil structure
- minimised soil exhaustion
- maintain a balance of nutrients
- reduce disease
The logic includes ideas such as. A leafy crop thrives on nitrogen, a legume crop fixes nitrogen in to the soil, so a leafy crop should follow a legume crop
A simple rotation chart would look like this
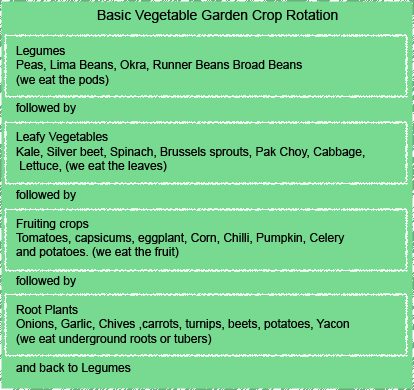
HOWEVER
Potatoes are in the same family as tomatoes, so potatoes should not follow tomatoes (use a different bed).
3 year charts and 4 year charts are both put forward, and different ideas as to what should follow what are also plentiful.
